'*** 밑에 분류 무시'에 해당되는 글 131건
- 2008.08.22 Israel
- 2008.08.20 강의정리, 강의자료: Digital signal processing: introduction, basic concepts
- 2008.08.19 TEXT: Digital and Analog Communication systems / Leon W. Couch
- 2008.08.18 강의노트, 강의정리 - communication system: chap 2. signals and spectra: overview
- 2008.08.18 chap 2. signals and spectra: useful wave characteristic
- 2008.08.17 TEXT(Ref.): optics
- 2008.08.16 공부는 동그란 원을 완성하는 과정
- 2008.07.23 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: Fourier analysis, PDEs: overview
- 2008.07.23 Fourier analysis, PDEs: Fourier analysis
- 2008.07.20 Fourier analysis of frequently used function
- 2008.07.19 Fourier analysis, PDEs: PDEs
- 2008.07.18 chap 2. signals and spectra: energy signal, power signal and spectrum
- 2008.05.17 internet access
- 2008.05.02 Difference equation에 대한 이해
- 2008.04.30 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: complex analysis: overview
- 2008.04.28 complex analysis: basic of complex number
- 2008.04.17 chap 2. signals and spectra: correlation, correlation function
- 2008.04.11 강의정리, 참고자료: detection and estimation theory: estimation theory - Bayes estimator
- 2008.04.10 강의정리, 참고자료: detection and estimation theory: estimation theory - ML estimator
- 2008.04.08 강의정리, 참고자료: detection and estimation theory: estimation theory - General overview
- 2008.04.03 강의정리, 참고자료: detection and estimation theory: detection theory - Bayes detector
- 2008.04.02 강의정리, 참고자료: detection and estimation theory: detection theory - NP detector
- 2008.03.25 강의노트, 강의정리: Mathemetics of modern engineering 2 (Complex number 1)
- 2008.03.21 강의노트, 강의정리: Mathemetics of modern engineering 2 (Complex number 2)
- 2008.03.16 battery: battery and button cell
- 2008. 8. 22. 11:32
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 8. 20. 15:16
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- TEXT: Digital and Analog Communication systems / Leon W. Couch
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 8. 19. 14:44

the subject of communication systems is immense.
what is communication system?
the communication systems are designed to transfer information between transmitter and receiver. however, noise limits our ability to communicate. communication systems are designed to transmit information bearing waveforms to the receiver. and there are many possibilities for selecting waveforms to represent the information.
communication system designers have four main concerns:
- selection of the information-bearing waveform
- bandwidth and power of the waveform
- effect of system noise on the received information
- cost of the system
- 1. introduction
- 2.
- Introduction, basic concepts (chap 1, 2)
* communication에 대해 말 그대로 개략적인 그림을 그리기
* 신호, 시스템등을 수학적인 표현으로 나타내기
* Fourier transform, Fourier series, sampling etc.
- Baseband signal processing and digital signaling (chap 3)
- Bandpass signal principles (and processing) and circuits
- Bandpass signal processing and digital modulated systems (chap 4, 5)
* AM, FM and other modulation
* from baseband frequency to bandpass frequency
* chap 3, 4, 5 는 course의 가장 핵심되는 내용들이 정리되어 있는 chapter 이다.
- chap 3 에서는 baseband signal processing 에 대해서. (이해를 돕기 위해 digital signal 예를 들었다)
- chap 4, 5 에서는 bandpass signal processing 에 대해서. (이해를 돕기 위해 analog signal 예를 들었다)
- 실생활에서 가장 빈번히 쓰이는 통신의 형태는 bandpass에서 일어나며 이는 analog signal이 될수도 있고, digital signal이될 수도 있다. chap 5 에서는 이렇게 실생활에서 빈번히 쓰이는 통신의 형태에 대해서 알아본다. (* 이 때 digital signal에 대한 기본적인 concept은 chap 3 에서 기초를 다지고 온다)
- digital signal에 대해서: digital signal은 analog signal에 조작을 가한 결과물이며, 이러한 조작과정(AD conversion) 에 대한 연구는 "digital and analog communication systmes (specific chap. 3)"을 기초로 한다.
Further Study
- "digital signal processing" 에서는 이런 조작과정 결과물(digital signal) 과 이를 처리할 system(digital system) 사이에서 일어나는 다양한 부분을 알아본다. "RF circuit design"의 첫부분에서는 analog signal과 digital signl 의 modulation/demodulation에 대해서 다시 한번 정리하게 된다.
supplement and solution: http://lcouch.us/
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Israel (0) | 2008.08.22 |
|---|---|
| 강의정리, 강의자료: Digital signal processing: introduction, basic concepts (0) | 2008.08.20 |
| 강의노트, 강의정리 - communication system: chap 2. signals and spectra: overview (0) | 2008.08.18 |
| chap 2. signals and spectra: useful wave characteristic (0) | 2008.08.18 |
| TEXT(Ref.): optics (0) | 2008.08.17 |
- 강의노트, 강의정리 - communication system: chap 2. signals and spectra: overview
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 8. 18. 12:00
chapter 2 는 signal에 대한 내용
this posting develops mathematical tools that are used to describe signals and noise from a deterministic waveform point of view. (the random waveform approach is given in chapter 6) the waveforms will be represented by derect mathematical expressions or by the use of orthogonal series representations such as the Fourier series.
properties of these waveforms, such as;
- DC value
- root-mean-square (RMS) value
- normalized power
- magnitude spectrum
- phase spectrum
- power spectral density
- bandwidth
- in addition, effects of linear filtering
will be established.
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 강의정리, 강의자료: Digital signal processing: introduction, basic concepts (0) | 2008.08.20 |
|---|---|
| TEXT: Digital and Analog Communication systems / Leon W. Couch (0) | 2008.08.19 |
| chap 2. signals and spectra: useful wave characteristic (0) | 2008.08.18 |
| TEXT(Ref.): optics (0) | 2008.08.17 |
| 공부는 동그란 원을 완성하는 과정 (0) | 2008.08.16 |
- chap 2. signals and spectra: useful wave characteristic
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 8. 18. 07:00
useful wave characteristic are the DC value, average power, and RMS value.
DC value
- the DC value of a wave is given by its time average, thus
- for any physical wave, we are actually interested in evaluating the DC value only over a finite interval of interest. in such a case, the DC value is
power
- for physics, power는 energy을 단위시간으로 나눈 물리양이다. 이러한 기본개념을 바탕으로 여러 다양한 분야에서 각 학문영역에 적용되어 활용되고 있다. electrical field의 경우 voltage와 current에 의해서 power와 energy를 정의한다.
it is known that power is defined as work per unit time, voltage is work per unit charge, and current is charge per unit time. this is the basic for the definition of power in terms of electrical quantities.
- the instantaneous power is given by
- the average power is
- if a load is resistive (i.e. with unity power factor), the average power is
- using RMS value concept,
RMS (root-mean square) value of
for the case of district function, formula become

for the case of continuous function, formula become

- computing average (normalized) power of sinusoidal waveform
using RMS value concept, RMS value of sinusoidal waveform is.
- concept of normalized power is assuming that is.
instantaneous normalized power is
average normalized power is
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TEXT: Digital and Analog Communication systems / Leon W. Couch (0) | 2008.08.19 |
|---|---|
| 강의노트, 강의정리 - communication system: chap 2. signals and spectra: overview (0) | 2008.08.18 |
| TEXT(Ref.): optics (0) | 2008.08.17 |
| 공부는 동그란 원을 완성하는 과정 (0) | 2008.08.16 |
| 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: Fourier analysis, PDEs: overview (0) | 2008.07.23 |
- 2008. 8. 17. 01:44
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 8. 16. 07:28
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: Fourier analysis, PDEs: overview
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 7. 23. 15:40
큰제목 Fourier analysis, PDEs 에 대한 내용
Fourier analysis concerns periodic phenomena, as they occur quite frequently in engineering and elsewhere. we can represent complicated (periodic) functions in terms of simple periodic functions, namely, cosines and sines. we call this infinite series as Fourier series.
- underlying ideas can be extended to nonperiodic phenomena. this leads to Fourier integrals and transforms. a common name for the whole area is Fourier analysis.
- in the most important of PDEs of physics and engineering is the area in which Fourier analysis has its most basic applications, related to boundary and initial value problems of mechanics, heat flow, electrostatics, and other fields.
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TEXT(Ref.): optics (0) | 2008.08.17 |
|---|---|
| 공부는 동그란 원을 완성하는 과정 (0) | 2008.08.16 |
| Fourier analysis, PDEs: Fourier analysis (0) | 2008.07.23 |
| Fourier analysis of frequently used function (0) | 2008.07.20 |
| Fourier analysis, PDEs: PDEs (0) | 2008.07.19 |
- Fourier analysis, PDEs: Fourier analysis
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 7. 23. 11:02
Fourier analysis
Fourier series
- periodic function
- a function is called a periodic function ifis defined for all real x (perhaps except at some points, likeand if there is some positive number p, called a period of, such that
- first few case, we will study various functions of period.
- given function of period , Fourier series
- given function of period can be represented by a trigonometric series; Fourier series,
- coefficients of Fourier series are the so-called Fourier coefficients of , given by the Euler formulas
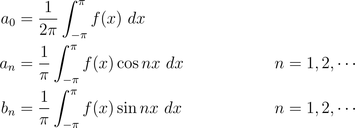
dddd
Fourier series expansion and function approximation
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 공부는 동그란 원을 완성하는 과정 (0) | 2008.08.16 |
|---|---|
| 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: Fourier analysis, PDEs: overview (0) | 2008.07.23 |
| Fourier analysis of frequently used function (0) | 2008.07.20 |
| Fourier analysis, PDEs: PDEs (0) | 2008.07.19 |
| chap 2. signals and spectra: energy signal, power signal and spectrum (0) | 2008.07.18 |
- Fourier analysis of frequently used function
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 7. 20. 16:04
sinc function



'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: Fourier analysis, PDEs: overview (0) | 2008.07.23 |
|---|---|
| Fourier analysis, PDEs: Fourier analysis (0) | 2008.07.23 |
| Fourier analysis, PDEs: PDEs (0) | 2008.07.19 |
| chap 2. signals and spectra: energy signal, power signal and spectrum (0) | 2008.07.18 |
| internet access (0) | 2008.05.17 |
- Fourier analysis, PDEs: PDEs
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 7. 19. 12:38
Partial Differential Equations (PDEs), terms for math 중 PDEs의 중요한 문제 type 참고
* 별도의 강의노트 없음
* 수업의 진행은 가장 simple한 형태의 wave equation(1D)과 heat equation(1D)에 대해서 알아본 다음 복잡한 형태의 case에 대해서 각각 진행을 하였음.
* 포스팅의 정리는 wave equation에 대한 모든 내용을 정리 후, heat equation에 대한 내용을 정리함.
lecture topic. 1D(x,t): string, vibrating equation
PDE의 정의와 solution of PDE (function) 을 정의하는 variables(시간 and 좌표)
PDE을 이용한 중요한 mathematical topic 중 vibrating string
vibrating string의 modeling을 통한 PDE 유도 + B.C. 적용 + I.C. 적용 => get solution
vibrating string의 modeling
through the separating variable, generate the two ODE
B.C. 적용: 2개의 B.C.을 2개의 ODE에 적용. linear property을 적용한 general solution을 구함.
I.C. 적용: general solution으로 부터 2개의 I.C.을 만족하는 solution을 Fourier series을 이용 get it!!
PDE vibrating string의 solution 분석; "For same answer, but totally different form"
- frequency analysis(fixed t, vary x 인 경우): foundamental harmonic, sub harmonic, node
- wave analysis: u(x, t)는 2개의 wave form이 right or left로 이동하는 결과
lecture topic. 1D(x,t) heat conduction
heat equation(PDE)의 유도 + B.C. 적용 + I.C. 적용 => get solution
case 1: B.C. u(0, t)=0, u(L, t)=0
heat equation의 modeling
through the separating variable, generate the two ODE
B.C. 적용: 2개의 B.C.을 2개의 ODE에 적용. linear property을 적용한 general solution을 구함.
I.C. 적용: general solution으로 부터 I.C.을 만족하는 solution을 Fourier series을 이용 get it!!
case 2: B.C. u(0, t)=U0, u(L, t)=U1: steady-state condition 고려
case 3: B.C. u_x(0, t)=0, u_x(L, t)=0: steady-state condition 고려
***
case 2에서의 w(x,t)=u(x,t)-vss(x)의 물리적인 의미
G(t)의 general solution 유도과정
lecture topic. 2D(x,y,t) vibrating equation
prerequisite concept
- Sturm-Liouville equation, Bessel's equation
*** Sturm-Liouville equa. 특징
- infinite number of eigenvalue and eigenfunction.
- eigenfunction are orthogonal over [a, b] w.r.t. the weighting function
*** Bessel's equa. 특징
-
subtopic. vibration of a circular
u=u(x, y, t); displacement of p(x, y) at time t.
- change coordinate system of PDE: from rectangular to polar
*** theta가 변수로서 의미를 갖지 못하게 되면서 u=u(r, theta, t)는 u=u(r, t)로 나타낼 수 있다.
- ODE의 eigen value을 찾아 general solution을 완성하는 과정
Sturm-liouville equation 형태로 변형
Bessel's equation (of order 0) 형태로 변형하여 eigen value 결정
2개의 ODE의 곱으로서 general solution 결정
- I.C.을 적용하여, a_n과 b_n 값을 결정
lecture topic. 2D(x,y,t) heat conduction
prerequisite concept
-
subtopic. heat conduction in a rectangle domain
electrostatic potential problem (HW 4, 12.5 28 참고)
subtopic. heat conduction in a circular domain
* refer. PDE (wave equation, heat equation) case별 공식정리
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Fourier analysis, PDEs: Fourier analysis (0) | 2008.07.23 |
|---|---|
| Fourier analysis of frequently used function (0) | 2008.07.20 |
| chap 2. signals and spectra: energy signal, power signal and spectrum (0) | 2008.07.18 |
| internet access (0) | 2008.05.17 |
| Difference equation에 대한 이해 (0) | 2008.05.02 |
- chap 2. signals and spectra: energy signal, power signal and spectrum
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 7. 18. 10:39
energy spectrum density (ESD)
- the ESD is defined for energy waveforms by
power spectrum (power spectrum density, PSD)
(FYI) chap 2. signals and spectra: useful wave characteristic, wave의 power에 대해 정리한 내용 참고.
- the PSD for a deterministic power waveform is
and
- Wiener-Khintchine theorm. PSD and autocorrelation function of certain physical waveform are Fourier transform pairs relation; that is
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Fourier analysis of frequently used function (0) | 2008.07.20 |
|---|---|
| Fourier analysis, PDEs: PDEs (0) | 2008.07.19 |
| internet access (0) | 2008.05.17 |
| Difference equation에 대한 이해 (0) | 2008.05.02 |
| 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: complex analysis: overview (0) | 2008.04.30 |
- internet access
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 5. 17. 04:34
Common method of internet access include
- dial-up
dial-up internet access
dial-up internet access is form of internet access via telephone line(telephone network). the client uses a modem connected to a computer and a telephone line to dial into an ISP's node to establish a modem to modem link, which is then routed to internet.
- modern dial-up modems typically have a maximum theoretical speed of 56 kbit/s1
- 상용 전화선의 음성 데이터 처리와 model rate 사이의 상관관계
voice 주파수 대역 및 max frequency에 따른 nyquist frequency 는 8KHz 로 결정되었다. 샘플링되는 음성 신호의 quantization level은 256개 로서 2의 8승 개에 해당된다. 따라서 초당 처리 bit 는 8 KHz * 8 bits = 64 Kbits/sec.
오랫동안 64 Kbits/sec 로 통신을 하다가 음성신호의 전송은 8 bit가 아니라 7 bit로도 충분하다는 것을 발견하였다. 하지만 이미 8 bit의 규약으로 인프라(회선)가 건설되었기에 7 bit는 voice 전송을 위해 1 bit는 administration 목적을 위해 사용하고 있다. modem 의 경우 56 Kbit/s가 이론적인 최고 속도 (using the V.90 or V.92 protocol)
- broadband internet access
broadband internet access (or just broadband) is high data rate internet access - typically contrasted with dial-up access over a 56k modem. it is often called 'high speed' internet.
- DSL: ADSL (asymmetric digital subscriber line)
DSL is a family of technologies that provides digital data transmission over the wires of a local telephone network. DSL can be used at the same time and on the same telephone line with regular telephone, as it uses high frequency, while regular telephone uses low frequency.
ADSL is a data communications technology that enables faster data transmission over copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband modem can provide.
landline
T-lines
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a trademark for certified products based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. this certification warrants interoperability between different wireless devices. the term Wi-Fi is often used by the public as a synonym for WLAN; but not every wireless Lan product has a Wi-Fi certification, which may be because of certification costs that must be paid for each certified device type.
- Wi-Fi logo and practical example


(우) router, unicorn WB-1500N 의 제품상자에 표시되어 있는 Wi-Fi 로고
- Wi-Fi 에 대한 좀더 자세한 정보에 대해서는 별도의 posting을 통해 정리한다.
satellite
cell phone
- Refer 강의노트, 강의정리: Comm theory and System: baseband signal processing [본문으로]
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Fourier analysis, PDEs: PDEs (0) | 2008.07.19 |
|---|---|
| chap 2. signals and spectra: energy signal, power signal and spectrum (0) | 2008.07.18 |
| Difference equation에 대한 이해 (0) | 2008.05.02 |
| 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: complex analysis: overview (0) | 2008.04.30 |
| complex analysis: basic of complex number (0) | 2008.04.28 |
- 2008. 5. 2. 12:56
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: complex analysis: overview
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 4. 30. 03:46
큰제목 complex analysis에 대한 내용
many engineering problems can be modeled, investigated, and solved by functions of a complex variable. for simpler problems, such as simpler electric circuits and mechanical vibrating systems, some acquaintance with complex numbers will suffice. for more complicated problems in heat conduction, fluid flow, electrostatics, etc., one needs the theory of complex analytic function, briefly called complex analysis.
comlex analysis의 최종 목적은 analytic function을 이해하고 활용하는데 있다.
그러기 위해서 기본적인 complex number의 정의부터 시작하여 논의를 시작한다.
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| internet access (0) | 2008.05.17 |
|---|---|
| Difference equation에 대한 이해 (0) | 2008.05.02 |
| complex analysis: basic of complex number (0) | 2008.04.28 |
| chap 2. signals and spectra: correlation, correlation function (0) | 2008.04.17 |
| 강의정리, 참고자료: detection and estimation theory: estimation theory - Bayes estimator (0) | 2008.04.11 |
- complex analysis: basic of complex number
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 4. 28. 15:14
definition of complex number
basic computation
representation of complex number
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Difference equation에 대한 이해 (0) | 2008.05.02 |
|---|---|
| 강의노트, 강의정리 - Eng. mathematics: complex analysis: overview (0) | 2008.04.30 |
| chap 2. signals and spectra: correlation, correlation function (0) | 2008.04.17 |
| 강의정리, 참고자료: detection and estimation theory: estimation theory - Bayes estimator (0) | 2008.04.11 |
| 강의정리, 참고자료: detection and estimation theory: estimation theory - ML estimator (0) | 2008.04.10 |
- chap 2. signals and spectra: correlation, correlation function
- *** 밑에 분류 무시
- 2008. 4. 17. 15:00
correlation
- in probability theory and statistics, correlation (ofter measured as a correlation coefficient) indicates the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two random variables. that is in contrast with the usage of the term in colloquial speech, denoting any relationship, not necessarily linear.1
correlation function
- correlation functions contain information about the distribution of points or events, or things across some space/time.2
- a normalized correlation function for functions of time can be defined as,
- auto-correlation function
different definitions of auto-correlation are in use depending on the field of study.4
auto-correlation,
- cross-correlation function
- for binary sequences, it turns out that can be determined relatively simply by noting that the variableis the number of bits or digits by which the second sequence is shifted with respect to the first. then by comparing the two sequences bit by bit, the normalized correlation function is determined from
좀더 mathematical derivation 을 원한다면, digital and analog communication system, p373을 볼 것.
'*** 밑에 분류 무시' 카테고리의 다른 글
- 2008. 4. 11. 00:29
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 4. 10. 12:11
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 4. 8. 14:17
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 4. 3. 03:30
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 4. 2. 03:48
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 3. 25. 09:38
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 3. 21. 01:12
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.
- 2008. 3. 16. 17:50
내용을 보시려면 비밀번호를 입력하세요.


 invalid-file
invalid-file PDE(waveandheatequation)공식정리.doc
PDE(waveandheatequation)공식정리.doc



Recent comment